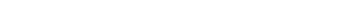Alternative Text (Alt Text)
Alternative text (alt text) provides a textual alternative to non-text content in web pages.
It is especially helpful for people who are visually impaired or cognitively disabled and rely on screen readers. Screen readers identify and interpret a website's content using text-to-speech, sound icons or braille output devices. Alt text is a crucial element for creating an accessible website. A successful, accessible website includes alt tags for every image.
It is especially helpful for people who are visually impaired or cognitively disabled and rely on screen readers. Screen readers identify and interpret a website's content using text-to-speech, sound icons or braille output devices. Alt text is a crucial element for creating an accessible website. A successful, accessible website includes alt tags for every image.
- Alt text images must be retyped in the alt text.
- All context and relationship between concepts in images must be explained in alt text.
- All relevant information in an image must be retyped.
- All metaphors in images need to be explained in alt text.
- Images for art history require the techniques to be mentioned.
- All data points in tables, charts, plots, graphs, and more need to be written in the alt text.
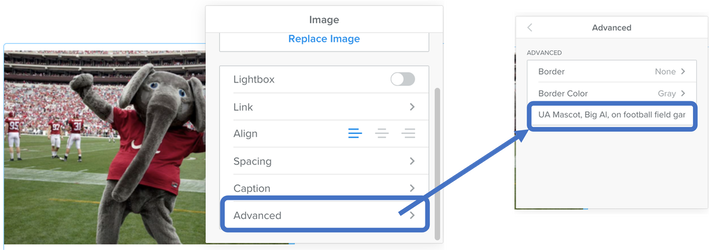
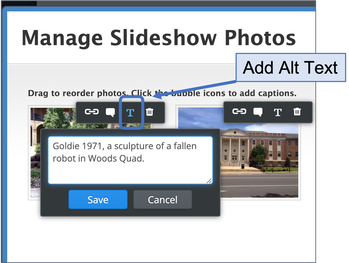
How to enter alt text for Singles Images, Slideshow Images, and Gallery Images
Single images added with the Image Element
Use the Advanced menu as shown below. DO NOT use the phrases "image of ..." or "graphic of ..." to describe the image. It is usually apparent to the user that it is an image.
Why add alt text?
|
Alternative text serves several functions:
|
Alternative text can be presented in two ways:
|
Decorative images do not present important content, are used for layout or non-informative purposes, and do not appear within a link. In almost all cases, spacer and decorative images should have null alt text (alt="").
Visit Alt Text Techniques for more information.
Visit Alt Text Techniques for more information.